Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Robotics are two cutting-edge technologies at the forefront of development in recent years. This article presents how the convergence of the two technologies is transforming different industries worldwide, as well as some examples of concrete applications.
The advancement of Artificial Intelligence pushes the operational capabilities of mobile robotics that are designed to be collaborative, autonomous and to perform tasks not only mechanically, but intelligently.
Many of the robots operating in different industrial environments have been developed to perform relatively simple, mechanical and repetitive tasks, but how about when more complex tasks are required, or when robots operate in unpredictable environments?
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE AND ROBOTICS
In this sense, AI impacts both the performance and functionality of autonomous mobile robots (AMR), potentially extending their capabilities in terms of adaptation and learning.
AI-enabled autonomous mobile robots are equipped with advanced deep learning algorithms that provide them with improved versatility while enhancing their productivity, reliability, efficiency and safety in collaborative environments.
Through these AI algorithms and machine learning techniques, these robots can perceive, interpret and respond to their environment autonomously and intelligently. This enables higher reliability for tasks such as detection, identification and classification of different objects, vehicles, humans or animals.
By detecting and recognising objects, the mobile robot will have better situational awareness and will navigate in crowded environments while avoiding collisions with obstacles.
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE AND PROCESS AUTOMATION
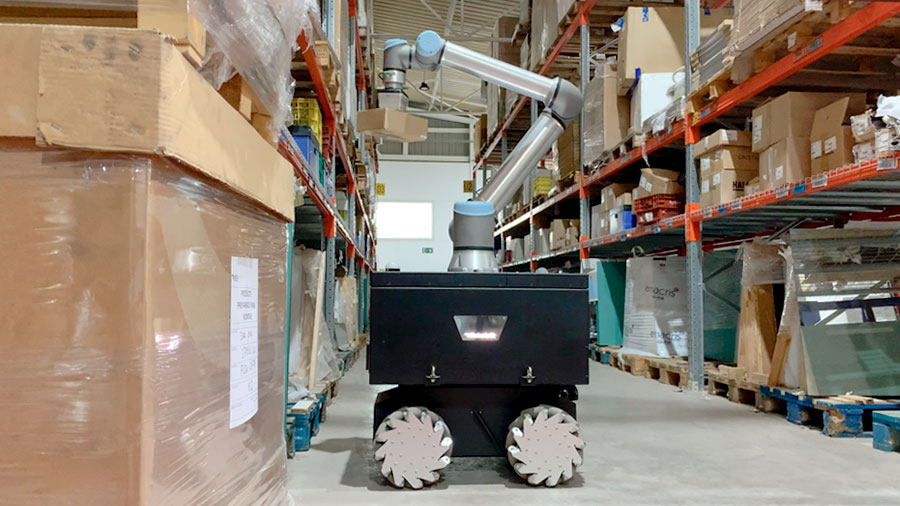
Detection technologies such as lidar, cameras or sensors enable mobile robots to collect data from the environment in real time, which is then processed and analysed by AI algorithms. One example is object detection and recognition: the RB-KAIROS+ mobile manipulator could quickly sort items, assess product quality, detect defects and speed up assembly processes, thanks to AI. In a logistics environment, this translates into higher product throughput, reduced errors and thus higher customer satisfaction.
Another example for process automation in a warehouse would be in relation to stock management. An AMR identifies and locates various products or items on the shelves, and can then update inventory databases and track stock levels. This helps to optimise the efficiency of the picking and replenishment processes.
This is especially relevant given the rise of e-commerce, which has accelerated the timescales for manufacturers and distributors, as well as the volume of production.
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE AND AUTONOMOUS NAVIGATION
Thanks to Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL), a subfield of AI, AMRs can now have navigation and path planning capabilities comparable to humans. They can navigate complex environments, avoid obstacles, optimise their routes efficiently and operate in dynamic and unpredictable environments such as warehouses, hospitals, car parks, factories or events held in large venues such as trade fairs or sporting events, where large crowds of people gather.
In short, collaborative mobile robotics integrating Artificial Intelligence is a powerful tool that improves the competitiveness of any sector thanks to the intelligent automation of tasks, a more accurate understanding of its environment and the enormous capacity to collect, analyse and process data collected from any of the environments.