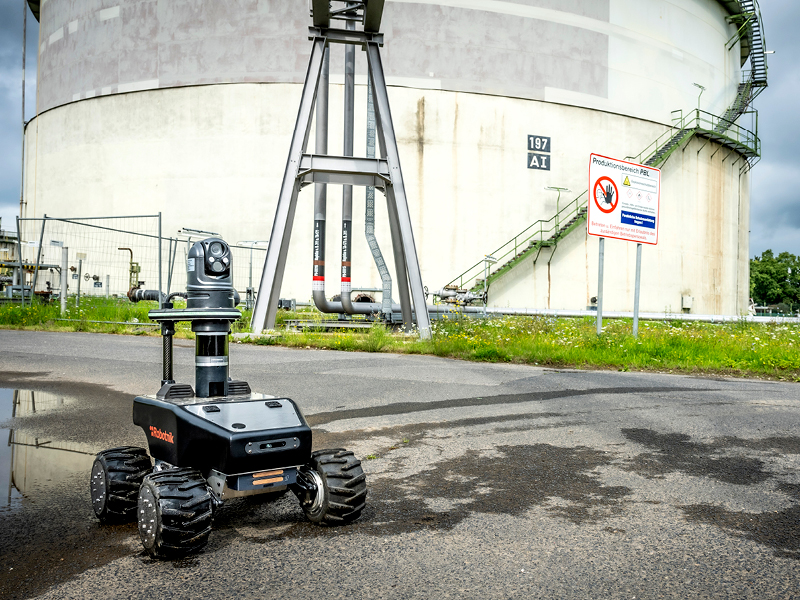
Industrial inspections are crucial to maintaining safety, efficiency and productivity in various sectors. Traditional inspection methods are often time-consuming, labour-intensive and present safety risks for human inspectors. However, the arrival of inspection robots has simplified industrial inspections, providing improvements in reliability and safety. From Robotnik’s experience with the inspection robot RB-WATCHER, this article reviews the advantages that autonomous mobile robotics provide in industrial inspection, what tasks or processes can be automated and what are the most in-demand applications/areas.

WHAT ARE INDUSTRIAL INSPECTIONS?
The systematic procedures within industrial inspections aim to evaluate the state of equipment, facilities and processes within an industry. These inspections are essential to ensure that industrial operations are carried out safely, efficiently and in accordance with current regulations. The main objectives of industrial inspections are:
- Safety: Identify and mitigate potential risks to the safety of workers and the environment.
- Operational efficiency: Ensure that equipment and systems operate optimally, minimising downtime.
- Regulatory compliance: Verify that all applicable regulations and industry standards are met.
- Preventive maintenance: To detect problems before they become failures, allowing planned maintenance.
- Quality control: Ensure that final products meet established quality standards.

INDUSTRIAL INSPECTIONS WITH AUTONOMOUS MOBILE ROBOTS
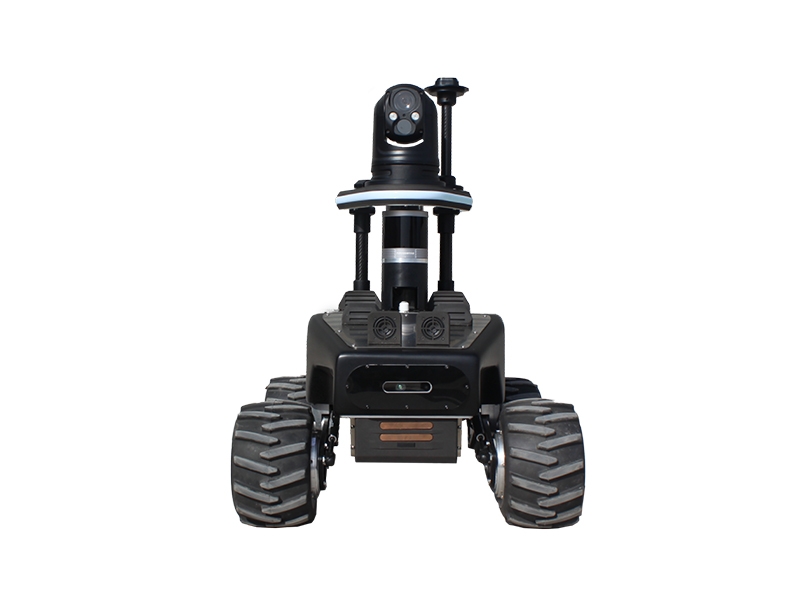
Inspection robots bring significant innovation in the field of industrial inspections. Equipped with advanced technologies, these robots can perform a variety of inspection tasks with high precision and efficiency.
How does an autonomous mobile robot automate industrial inspection?
1. Autonomous navigation
Autonomous mobile robots are equipped with advanced navigation systems that allow them to move independently through industrial environments. They use technologies such as LIDAR, GPS and advanced vision systems to:
- Create 3D Maps of the Environment: Allowing you to plan optimal inspection routes.
- Avoid Obstacles: Detecting and avoiding obstacles in real time.
- Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM): To navigate in unknown environments and continually update your maps.
2. Data collection and analysis by robotic inspections
During an industrial inspection, autonomous mobile robots collect large amounts of data that are:
- Transmitted in Real Time: To a control centre where engineers can monitor and analyse the results instantly.
- Stored for Later Analysis: Allowing more detailed analysis and identification of trends over time.
3. Interaction and communication in industrial inspection robots
Inspection robots can be connected to communication systems that allow them to:
- Receive remote instructions: From a control centre or an operator.
- Report incidents or anomalies: Immediately, alerting those responsible for maintenance.
- Collaborate with other robots: Coordinating with other robots to perform more complex inspections efficiently.
USE CASES: INDUSTRIAL INSPECTION WITH AUTONOMOUS MOBILE ROBOTS
Here you can check out the robot use case RB-WATCHER performing industrial inspections in an electrical substation of the Spanish energy company EDP. Inspection robots also automate industrial inspections in the following areas:
Oil and Gas Industry Inspection robots
Industrial inspection in the oil and gas industry takes on special relevance due to the nature of the materials and the damage caused by any error in this sector. Inspection robots are used, for example, to detect leaks, monitor storage tanks or offshore platforms. An inspection robot can operate in hazardous environments such as those containing high levels of toxic gases.
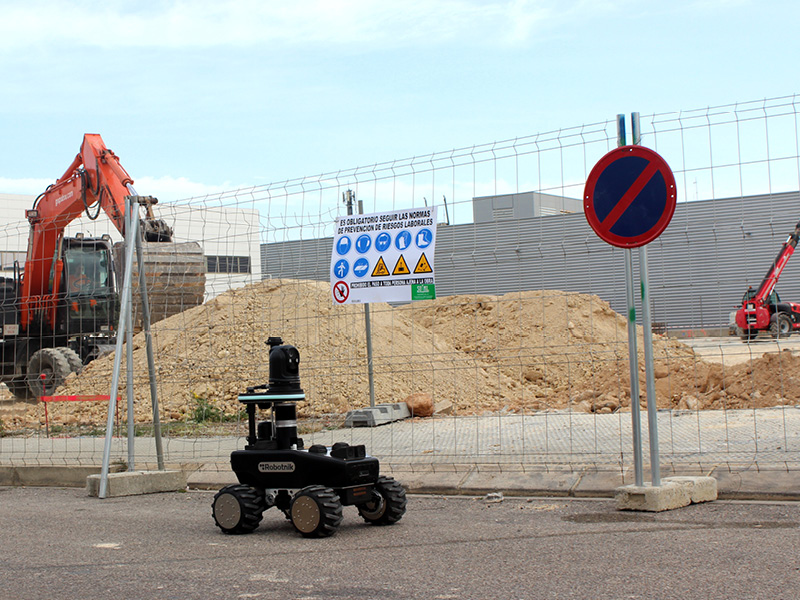
Infrastructure inspection with robots
Evaluating the condition of bridges, tunnels and other infrastructure or construction environments.
Renewable energies and industrial inspection robots
Inspection robots are increasingly used for the maintenance of renewable energy infrastructures such as wind turbines and solar panels. In these environments, an autonomous mobile robot can identify problems such as erosions, cracks and misalignments in equipment or detect hot spots.
Warehouses and logistics centres using autonomous inspection robots
Monitoring and checking that the storage systems and logistical or production material are working properly. Furthermore, an inspection robot can also perform inspection in a warehouse in terms of detecting intrusions, anomalies and even perimeter inspection in the case of RB-WATCHER.
IMPROVING INDUSTRIAL INSPECTIONS WITH MOBILE ROBOTS
Inspection and maintenance robots have significantly improved the way industrial inspection tasks and processes are performed. They can navigate autonomously or be controlled remotely, offering several advantages over traditional inspection methods.
Flexibility and Accessibility of Industrial inspection robots
Mobile robots can navigate complex industrial environments, reaching areas that are difficult or dangerous for human inspectors. This flexibility allows for comprehensive inspections even in large facilities.
Real-Time Data Collection by autonomous inspection robots
Mobile robots can transmit inspection data in real time, allowing immediate analysis and decision-making. This capability is particularly valuable for quickly identifying and addressing problems.
Cost Effectiveness of robotic inspections
By minimising downtime, mobile robots can significantly reduce costs associated with industrial inspections. This profitability makes them an attractive option for industries of all sizes.
Enhanced Capabilities of industrial inspection robots
Robotnik inspection robots are equipped with a variety of sensors, such as thermal cameras, PTZ cameras or 3D LIDAR, improving their ability to detect a wide range of problems. This versatility makes them suitable for various inspection tasks.
THERMAL INSPECTIONS WITH MOBILE ROBOTS
One of the most in-demand tasks is autonomous thermal inspection using mobile robots. Within general industrial inspection, thermal inspections are a critical part of industrial maintenance. Detecting anomalies such as overheating, insulation faults or electrical faults ensures that they are rectified before becoming more serious problems. Inspection robots integrate thermal imaging cameras to carry out these inspections in an uninterrupted, stable and effective way, avoiding errors derived from human fatigue.
Advantages of thermal inspections with autonomous mobile robots
- Precision and Accuracy: Inspection robots with thermal cameras capture high-resolution thermal images, allowing for accurate detection of temperature variations. This accuracy is essential to identify potential problems that could lead to equipment failure or dangerous situations.
- Safety: Thermal inspections often involve inspecting high-temperature equipment or hard-to-reach areas. Robots can safely navigate these environments, reducing risk to human inspectors.
- Efficiency: Robots can perform constant thermal inspections without interruption, minimising downtime in operations. This efficiency translates into a significant cost reduction for industries.
- Data collection and analysis: RB-WATCHER collects and stores large amounts of thermal data, which can be analysed to predict maintenance needs and prevent unplanned outages. This predictive maintenance capability is a significant advantage for industries looking to optimise their operations.
FUTURE OF INDUSTRIAL INSPECTION: SECURITY AND AUTOMATION
Technological evolution allows inspection robots to currently have improved capabilities to perform inspection and maintenance tasks with a precision and reliability that was hitherto unfeasible.
Thus, Inspection robotics have totally changed the landscape of industrial inspections, offering a safer, more efficient and profitable automated solution.
In conclusion, the future of industrial inspection presents a clear trend towards the use of mobile devices that allow the automation of critical tasks that present obvious dangers for operators. Thanks to their ability to navigate complex terrain, mobile inspection robots execute tasks with high precision and analyse large volumes of data, allowing failure prediction.
With continued advances in artificial intelligence and robotics, inspection robots will increase their capabilities, more intelligently automating industrial inspections.

FAQs about robotics
Robotnik develops its own software for mobile robotics based on the open source operating system ROS.
Robotnik’s software department is involved in many of the robot development and manufacturing processes: from functionality updates to Artificial Intelligence integration.
Some current trends in robotics software include AI, Machine Learning or Natural Language Processing.


