Innovation in terms of robotics applications in agriculture has advanced considerably in the last 5 years.
The objective of agricultural robotics is to help the sector in its efficiency and in the profitability of the processes. In other words, mobile robotics works in the agricultural sector to improve productivity, specialization and environmental sustainability.
Labor shortages, increased consumer demand and high production costs are some of the factors that have accelerated automation in this sector, with the aim of reducing costs and optimizing harvests.
Did you know that up to 99% of phytosanitary products are currently wasted because they cover the entire field? Agricultural robotics is capable, for example, of spraying pesticides only to the plants that need them. This is just one example of how very concrete benefits can be seen in sectors that are traditionally not very automated.
The incorporation of robotics in agriculture improves both productivity and working conditions for farmers and workers. Intelligent systems are becoming the ideal solution to drive precision agriculture. Today, a large number of agricultural operations are already being done autonomously.
Thus, collaborative robots are now commonly used in fruit harvesting or insect grafting and cultivation, where Artificial Intelligence provides predictive data to optimize farms and plantations.
Types of robots used in agriculture
These are some applications of robotics in agriculture for which Robotnik robots are used:
- Crop condition identification and corresponding chemical application, spraying or harvesting, as required by the fruit or plant.
- Mobile manipulation through collaborative arms (harvesting, fruit handling).
- Collection and conversion of useful information for the farmer.
- Selective application of pesticides.
- Selection to avoid food waste
R&D for agricultural robotics
Since 2002, Robotnik has participated in more than 60 research projects, most of them at European level. Currently, some 30 projects of different nature are underway: some with objectives oriented to logistics, others to the health sector or also to the agri-food sector, among others. This makes it possible to use intelligent, autonomous and collaborative mobile robots that enable the creation of more efficient industrial processes with a better use of resources, which translates into higher productivity in general.
Examples of agriculture robotics R&D projects in which Robotnik is involved:
BACCHUS: Mobile Robotic Platforms for Active Inspection and Harvesting in Agricultural Areas.
BACCHUS intelligent mobile robotic system promises to replicate manual harvesting operations, while eliminating manual labor by operating autonomously on four different levels:
- The robot autonomously navigates to inspect crops and collect data from the agricultural area through its integrated sensor system.
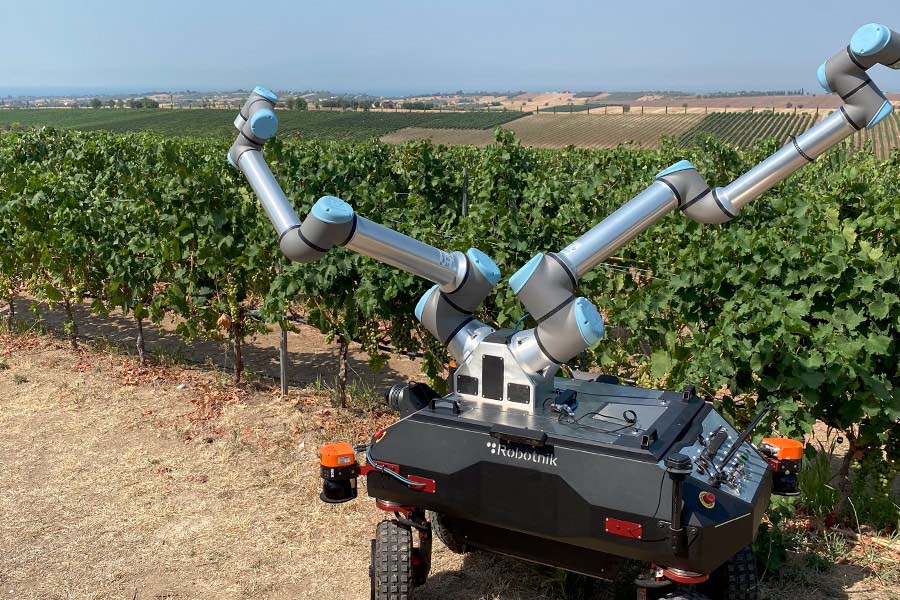
- The robot performs bi-manual harvesting operations with the finesse required by the environment.
- Additive manufacturing is employed to adjust the robot gripper to the geometry of different crops.
- Presentation of advanced cognitive capabilities and decision-making skills.
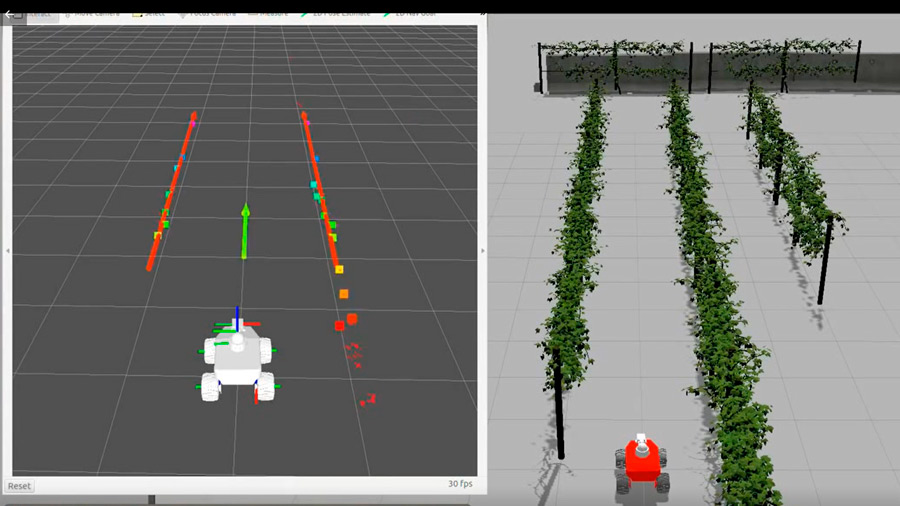
This R&D project employs the RB-VOGUI autonomous mobile robot with two fully integrated arms. The platform is used to develop a solution for grape harvesting in vineyards.
AGROBOFOOD: Digital transformation of the European agri-food sector through the adoption of robotic technologies.
Through robotics applications in agriculture, it aims to accelerate the digital transformation of the European agri-food sector. It will consolidate, expand and strengthen the current ecosystem by establishing a sustainable network of DIHs (Digital Innovation Hubs).
Robotnik is leading the experiment based on the SUMMIT-XL outdoor mobile platform, which is equipped with a series of sensors that will be used to collect information from the environment of an olive grove to maximize the olive yield.
COROSECT: Cognitive robotic system for digitized insect farms.
Agricultural robotic application to optimize insect production facilities as a possible solution to the environmental impact of high meat consumption.
The project will use state-of-the-art robotic equipment and artificial intelligence technologies to automate production. The project focuses on the idea of setting up dynamic work cells, where a single human worker will be assisted by several robots equipped with artificial intelligence algorithms and intelligent sensors at different stages of insect production.