The recycling of electronic waste (E-Waste) is currently the biggest threat to the planet, according to the Global Recycling Foundation.
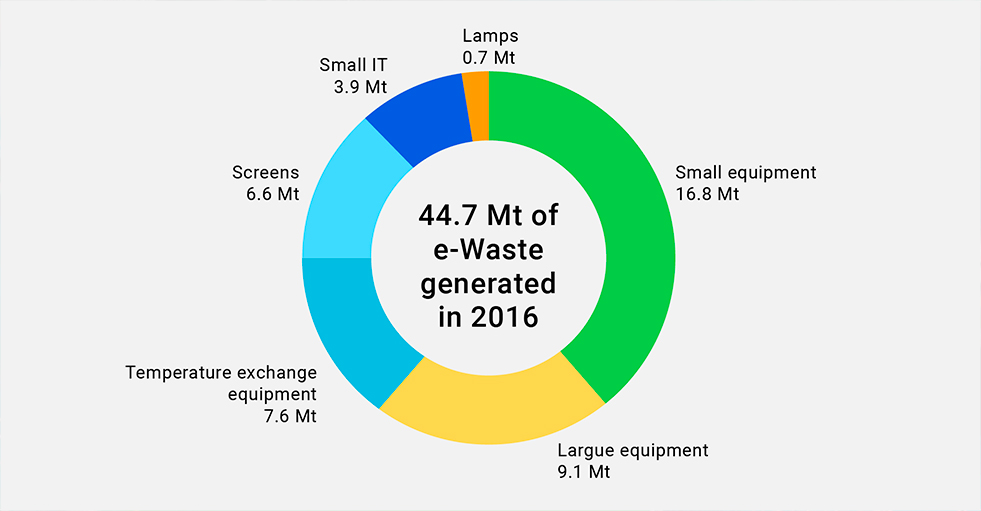
In fact, the United Nations recently warned that e-waste is considered to be the “fastest growing waste stream in the world”; we are actually talking about around 53 million tonnes per year (according to the UNU Global E-waste Monitor 2020 report, in 2019), which will increase considerably in the coming years, including toxic components and hazardous waste if not properly recycled.
The recycling of WEEE is a time and effort consuming process, due to the variety of devices to be recycled and the different components and materials they are made of. In the face of this reality, we, the industries, cannot remain on the sidelines.
Robotnik wants to be part of the solution and therefore, we participate in HR-RECYCLER, a multidisciplinary project which aims to improve the recycling capacity of European countries.
Human-robot collaboration in the WEEE recycling process.
A key issue in recycling processes is the routing of raw and disassembled materials and components through the recycling plant. This is a resource-consuming process, as materials and components are processed in various parts of the factory. In a typical recycling process, unsorted devices arrive at the recycling plant in large trucks. After sorting, each device has to be transported to its recycling station where it is separated into its components. The components can be further separated or ready to be moved to their final destination.
This is where Robotnik comes in. Transporting materials within a factory has to be done affordably, efficiently and safely. Furthermore, with the advent of the fourth industrial revolution, mobile robots have to be able to operate in collaboration with humans sharing the same space.
How to make it affordable?
Affordability is achieved by providing a mobile robot capable of transporting the same baskets that the factory already has, which reduces the number of changes that need to be made in the factory.
How to make it really efficient?
Efficiency is achieved through state-of-the-art navigation algorithms, as well as factory planning algorithms in general. Collaboration is achieved through the use of human-aware navigation, but also by increasing communication between the robot and the human about the robot’s intentions. Safety is achieved through the application of stringent measures, sensors and actuators that comply with the latest safety standards.
All this effort is directed by Robotnik towards the creation of a new robot: RB-ARES. Robotnik has developed a reliable solution that integrates robots, localization systems, configuration and programming tools (HMI) and Fleet Management System (FMS). This knowledge will be integrated into the new RB-ARES, which is able to carry up
to 1.500 Kg. and make a completely autonomous navigation.
Application of the RB-ARES robot in in recycling.
The purpose of RB-AREs will be to pick and place EURO pallets at ground level and direct them through the factory with the required features of affordability, efficiency, safety and collaboration with people. To fulfil this mission, RB-Ares is equipped with state-of-the-art actuators and sensors.
RB-ARES is powered by ROS, as well as Robotnik’s own technology for navigation, localization and human-machine interface, which allows easy configuration, programming and integration of the robot into different applications and fleet management systems, as is required by Industry 4.0. This is the main feature of Collaborative Mobile Robots like RB-ARES, an intelligent mobile robot that assists humans in a shared workspace and supports the optimisation of processes within the industry.
[1] World Economic Forum. (2019). A New Circular Vision for Electronics: Time for a Global Reboot, (January), 24. Retrieved from