Global competition in production has accelerated the need for automation in industry. Robot manipulators such as the RB-KAIROS+ streamline with precision the assembly processes in manufacturing companies. This article shows how assembly robots are a driver for assembly lines in different industries. Learn more about robotics assembly and the assembly tasks that a mobile manipulator can perform.

BENEFITS OF MOBILE MANIPULATOR ROBOTS FOR ASSEMBLY
In the manufacturing and industrial production sectors, efficiency is key. This efficiency involves achieving a reduction in time, increasing production speed and maintaining quality standards.
One of the most frequent, repetitive and demanding tasks is assembly. In industry, the assembly process involves putting together different parts to make a finished product. Many industries are aiming to automate assembly lines because it is not only highly precise but also a repetitive process.
Human intervention in assembly can not only slow down the pace of production, but also increases the potential for errors during manufacturing. These errors represent a significant risk to quality and higher economic costs.
Robotics assembly operations offers a number of benefits:
- Flexibility: Mobile manipulators can easily adapt to changes in the product design or assembly process, allowing them to perform a greater number of tasks in different locations.
- Efficiency: By eliminating the need to transport parts and components from one location to another, mobile robots reduce downtime and optimize production time.
- Space Optimization: RB-KAIROS+ can navigate tight spaces and work in areas of the production floor that might be difficult or impossible to reach for a fixed manipulator arm.
- Safety: Mobile robots are equipped with advanced sensors and navigation systems that allow them to avoid obstacles and operate safely in environments shared with workers.
- Cost reduction: although an initial investment is required, in the medium term, assembly robots reduce operating costs by increasing productivity and reducing errors in assembly.
INDUSTRIES BENEFITING FROM THE USE OF ROBOTIC ASSEMBLY
Many industries use robotic assembly, ranging from automotive to electronics, aerospace to food. A mobile manipulator is used in different ways to perform precise and efficient assembly tasks, depending on the specific needs of each industry. Here are some of the sectors that implement mobile manipulator robots in assembly processes:
- Automotive industry: the use of robotic manipulators in the automotive sector is among the most widespread. Robots are used to assemble a wide range of components, from engines and transmissions to car bodies and electronic systems. This mobile robot manipulator performs tasks such as welding, parts assembly, painting and material handling.
- Electronics: In the manufacturing of electronic products, such as mobile phones, computers and medical devices, manipulator robots are used to assemble small, delicate components with millimeter precision. These robots can place chips, solder components, assemble printed circuit boards, and perform quality testing, ensuring the reliability and performance of electronic products. ASSEMBLY ROBOT EXAMPLE - ELECTRONIC.
- Aerospace: A manipulator robot in the aerospace industry can assemble aircraft components, such as wings, fuselages, and propulsion systems. These robots can perform complex tasks in controlled environments, such as handling composite materials and high-precision welding, ensuring safety and quality in aircraft manufacturing. ASSEMBLY ROBOT EXAMPLE.
- Food industry: In the food industry, manipulator robots are used to assemble products such as food packages, cardboard boxes, and packaging trays. These robots can handle food hygienically and safely, reducing the risk of contamination and ensuring food quality and safety at all times.
In addition to the mentioned industries, the use of mobile manipulator robots has also spread to sectors such as the pharmaceutical industry, the plastics industry, the furniture industry and many others. These robots can perform a wide range of assembly tasks, from placing caps and labels to joining structural components, adapting to the specific needs of each application.
KEY APPLICATIONS OF ASSEMBLY ROBOTS IN MODERN MANUFACTURING
Mobile manipulator robots play a crucial role in various applications within an industrial assembly process, including:
- Small Parts Assembly: Small parts assembly involves the delicate handling and placement of components of very small dimensions within a final product. The mobile robot manipulator precisely picks the parts from a storage container and places them exactly where they are required in the assembly and then secures the parts in place using appropriate fastening methods, whether welding, gluing or other joining methods.
- Classification and selection: the identification and separation of different types of components based on their distinctive characteristics. Using advanced vision systems and sensors, the robot recognizes and classifies parts based on their shape, size, color or other specific properties. Once identified, it proceeds to automatically select the parts necessary for assembly, classifying them as required and optimizing the workflow.
- Pick & Place: The mobile manipulator robot can pick up individual parts from a storage container and transport them to the assembly station. This includes the precise selection of electronic, mechanical or any other components necessary for assembly.
- Placing and fixing components: Once the robot has transported the parts to the assembly station, it can place them in their correct position within the product being assembled. This involves precisely aligning components and securing them using screws, adhesives, or other fastening methods.
- Soldering: To assemble electronic components, the manipulator robot can perform welding tasks, whether spot welding, surface welding, or soldering components through the printed circuit board.
- Quality Inspection: The mobile manipulator can perform quality inspection tasks to verify that all parts are correctly assembled and working as intended. This may include functional testing, strength testing, and checking dimensional tolerances.
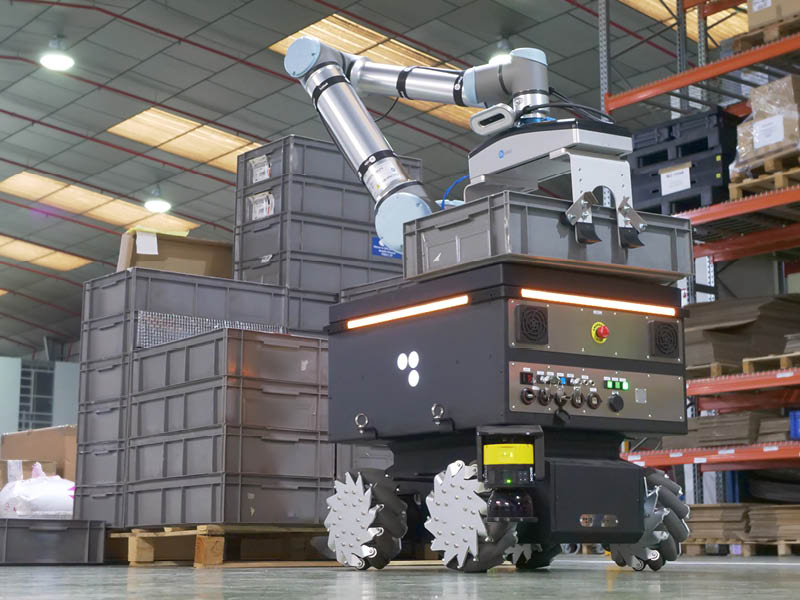

FUTURE OF INDUSTRIAL ASSEMBLY: INNOVATION AND AUTOMATION
Finally, technological advances and trends that are shaping the future must be taken into account. Innovations in artificial intelligence, IoT, machine vision, navigation and sensing sensors are rapidly enhancing the ability of mobile assembly robot handlers. They now quickly adapt to changing environments, collaborate safely with human workers and perform increasingly complex tasks with greater accuracy and efficiency.
The growing demand for custom-made products and the rise of e-commerce has created the need for more flexible production schemes. Companies must update their operations to support modern production methods by digitizing them, rather than sticking to outdated assembly line models. This adaptation is necessary to thrive in the new business environment. By embracing digital technologies, companies can improve efficiency and stay competitive in the market. This shift towards digitization is crucial for companies to remain relevant and successful in today’s fast-paced business world. In this context, robotic assembly solutions play a crucial role in automating.
Thus, more and more industries are betting on assembly robots to automate production lines with the aim of minimizing both errors and downtime and optimizing profitability.
FAQs about robotics
Assembly robots are automated machines designed to assemble (join or mount) components and products on production lines.
They can perform tasks such as welding, screwing, component placement and quality inspection.
Industries such as automotive, electronics, aerospace and general manufacturing use robots for assembly.


