Mobile robotics in the industrial and logistics sectors is proving to be a game-changer, offering unprecedented efficiency and productivity.
This article presents an overview of how mobile robots are transforming these activities, how to integrate them with existing factory automation systems, the different types available, and factors to consider when choosing a mobile robot.
Thus, logistics robotization and supply chain robotization is, basically, an open way to make the production process more profitable.
MOBILE INDUSTRIAL ROBOTS IN LOGISTICS AND SUPPLY CHAIN EFFICIENCY
With the introduction of mobile robots, there have been a number of significant benefits in the logistics and supply chain industry. These robots offer unprecedented flexibility in performing a variety of tasks, from transporting goods to warehousing and order picking.
The biggest benefit of mobile robots in logistics is improved operational efficiency. By automating repetitive but necessary tasks in logistics processes, mobile robots enable companies to optimize their processes and reduce delivery times. In addition, human resources are freed up to perform higher value-added activities.
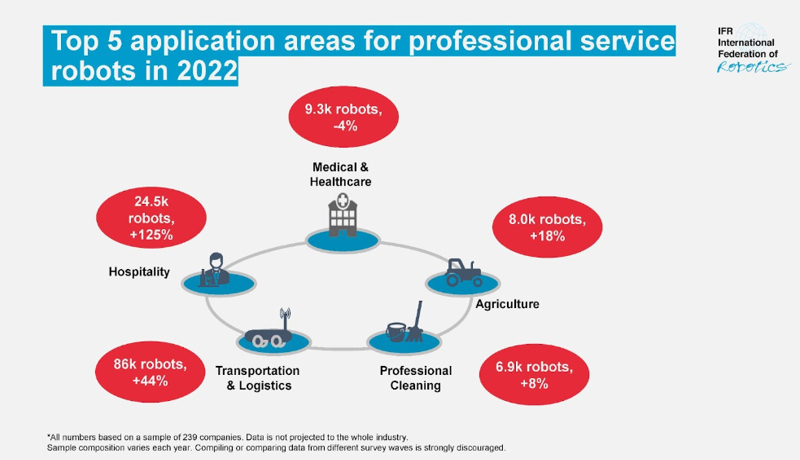
As a recent IFR report showed, transportation and logistics remains the area with the highest use of service robots.
ENHANCING SUPPLY CHAIN AUTOMATION WITH ADVANCED ROBOTICS SOLUTIONS
One of the main contributions of mobile robots to the logistics industry is the precision and consistency that robotics brings to the supply chain.
Robotnik’s mobile robots are equipped with advanced navigation systems and sensors that allow them to move safely and accurately in dynamic and changing environments, reducing errors and increasing service quality.
Automating the supply chain is a key objective for most logistics companies. Autonomous mobile robotics are helping to automate supply chain tasks from assembly line tending to stock distribution and sorting to transporting goods from storage.
KEY BENEFITS OF SUPPLY CHAIN AUTOMATION WITH MOBILE INDUSTRIAL ROBOTS
Robotics in supply chain offers some advantages when automating a logistics industry:
- Accuracy: the ability to have real-time, error-free inventory management updates ensures greater control and traceability.
- Uninterrupted supply: The stable and continuous supply of a production line is one of the tasks that an autonomous mobile robot can automate. In this way, the production flow is not interrupted at any time.
- Product quality: Usually, it is thought that in order to increase the profitability of a production environment, the quality of the product must decrease. However, the automation of certain processes by means of robots, allows that the quality of the product is not affected since the profitability is given by the constant and uninterrupted rhythm that a robot can maintain.
- Flexibility: A mobile industrial robot adapts to the production needs of each moment, both in peaks and in a decrease in demand.
HOW DO MOBILE ROBOTS INTEGRATE WITH EXISTING AUTOMATION SYSTEMS IN FACTORIES?
Real, reliable and stable technological integration remains a complex challenge today, although progress in recent years has been remarkable.
Integrating mobile industrial robots with existing factory automation systems maximizes efficiency and profitability. These robots are designed to complement and improve manufacturing and logistics processes by working with other automated equipment and systems.
One of the ways in which mobile robots integrate with existing systems is through communication and coordination with other devices or machinery. Mobile industrial robots can be connected through industry-standard interfaces, such as OPC UA or MQTT, allowing them to exchange data and receive instructions from other control systems in the factory.
In addition, mobile robots can be managed and supervised through fleet management systems, which allow operators to monitor and control multiple robots from a centralized location. This facilitates the cooperation of tasks performed by the robots and optimizes the allocation of resources in the factory.
Modularity is another feature for integrating mobile robots into existing manufacturing environments. These autonomous mobile robots are adaptable to a wide variety of applications, as they can be configured with different tools and accessories according to the specific needs in the production environment.
EXPLORING THE DIFFERENT TYPES OF MOBILE ROBOTS FOR OPTIMIZED LOGISTIC OPERATIONS
There are several types of mobile robots available on the market that automate the industry and supply chain. Here are some examples:
- Wheeled Mobile Robots: These robots use wheels to move around the environment and are ideal for conveying and load handling applications in warehouses and distribution centers.
- Mobile robots with arm: The so-called Autonomous Mobile Manipulators integrate a robotic arm on the mobile platform that allows them to perform handling tasks such as picking products or assembling components at different points of a production line.
- Autonomous Mobile Robots: For a robot or mobile manipulator to be considered autonomous, it must be equipped with advanced navigation systems and sensors that allow them to move autonomously in dynamic environments and without the need for direct human supervision.
- Collaborative mobile robots: These are designed to work safely alongside human workers, sharing the same workspace and collaborating on tasks such as transporting materials or picking orders.
Deciding on the appropriate type of mobile robot will depend on the specific needs of the application, including the type of load to be handled, the operating environment and safety requirements.

CHOOSING THE RIGHT MOBILE INDUSTRIAL ROBOT: FACTORS TO CONSIDER FOR YOUR APPLICATION
When it comes to choosing a mobile robot for a specific application, it is important to take into account some key factors to ensure the project’s success:
- Payload capacity: It is critical to choose a mobile industrial robot that can handle the payload required for the application, taking into account both the weight and dimensions of the objects to be handled.
- Operating environment: The environment in which the mobile robot will operate will have a significant impact on its performance and durability. It is important to consider factors such as the floor surface, the presence of obstacles or the ambient temperature.
- Navigation and safety: Navigation and safety systems are crucial to ensure that the mobile robot can move safely and efficiently in its environment. It is important to select a robot with advanced sensors and robust navigation algorithms.
- Integration with existing systems: The ability to integrate the mobile robot with the plant's existing automation and control systems is essential to maximize its efficiency and profitability. It is important to select a robot that is compatible with the interfaces and communication protocols used in the factory.
CONCLUSION
To summarize, the different types of mobile robots are transforming the industry and the supply chain, offering a number of benefits in terms of operational efficiency.
These benefits could be summarized as: automation of logistics processes, reduced errors and increased manufacturing flexibility.
Although full automation of supply chains is still a long way off, the logistics sector is one of the fastest industries to integrate mobile robotics as part of the path to more agile, efficient and cost-effective production.
Autonomous mobile robots and the future of the sustainable supply chain go hand in hand.
Let’s talk about how to automate your logistics environment?
FAQs about robotics
Some of the benefits that mobile robotics bring to the supply chain are precision, uninterrupted supply chain supply or adaptation to production demand.
Mobile robots are integrated with other logistics systems through the connection of interfaces such as OPC UA or MQTT to coordinate information and actions.
You should take into account characteristics such as the load to be handled, the type of operating environment or the required safety factors.




