Automation and robotics are already part of the daily life of numerous industries that have managed to streamline, make profitable and optimize many of the internal processes. These are two different but closely related concepts.
Currently, most automation projects rely on robotics.
This article shows an overview of what robotics is, what automation is, the differences between robotics and automation and what are the real advantages they bring to society.
DEFINING ROBOTICS AND AUTOMATION: WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW?
What is robotics and what is automation? Robotics is an interdisciplinary scientific field that combines different engineering, computer science, and other disciplines to design, build, and operate robots. A robot is a programmable machine capable of carrying out tasks autonomously, in the case of Robotnik, or semi-autonomously.
On the other hand, automation refers to a broader concept that involves using technology to perform tasks automatically, without direct human intervention. This may include the use of robots, but also encompasses other types of automatic systems, from simple timers to complex industrial control systems.
KEY DIFFERENCES BETWEEN ROBOTICS AND AUTOMATION
While automation and robotics often go hand in hand, there are key differences between them. The main distinction lies in the focus and functionality of each one.
Robotics focuses on the design, construction and programming of specific robots to perform particular tasks. Robots can be mobile or static, and their design adapts to the needs of the task they intend to execute. For example, a manipulator robot is designed to assemble components on a production line, while a domestic robot vacuum floors or mows lawns.
On the other hand, automation refers to the process of automating tasks using technology, which can include robots but is not limited to them. Automation can involve the programming of computer systems, specific software for the control of industrial processes, the implementation of building control systems and much more.
Usually, robotics pursues the goal of automating tasks or processes. However, robotics is a subset of automation that focuses specifically on the development and manufacturing of robots.
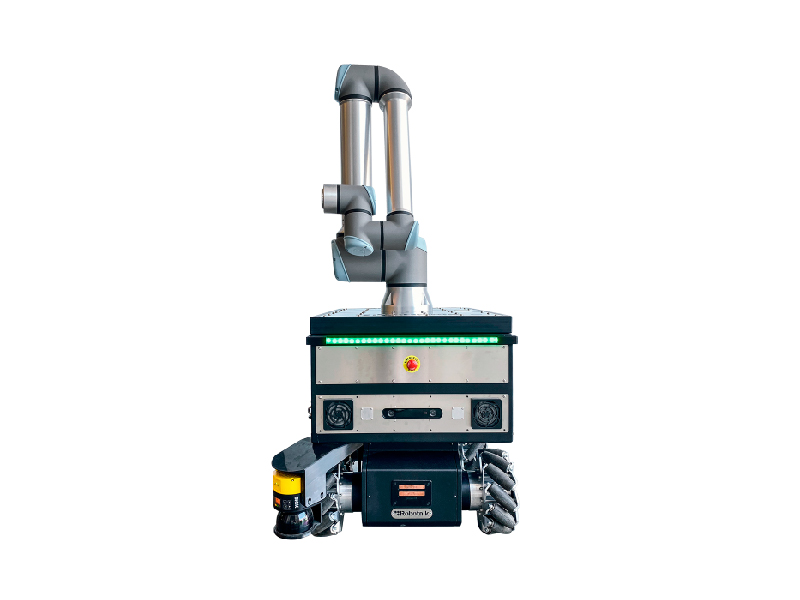

AUTOMATION VS ROBOTICS: APPLICATIONS AND BENEFITS
It’s not so much about which one is better, but how they complement each other. Automation and robotics are tools that can be used together or separately, depending on specific needs and objectives.
An automation project for an industrial environment can include a set of tools and technologies that, together, manage to optimize manufacturing processes.
For example, factory automation can include software for controlling, monitoring and managing customers, a robotic platform that works autonomously in the warehouse area to transport loads, and a mobile manipulator robot that constantly performs pick & place tasks, pick & place tasks, assisting in stock control.
If the example is in a domestic environment, automation can involve the control of security, lighting and air conditioning systems, while robotics would be responsible for automating domestic tasks such as cleaning, cooking or assisting the elderly.
BENEFITS AND ADVANTAGES OF AUTOMATION IN INDUSTRY 4.0
Automation offers a number of benefits for both companies and workers. Here are some of the reasons why automation is a process that more and more types of industries are betting on:
- Increased efficiency: Automated systems allow tasks to be executed more quickly, which increases productivity and reduces operating costs.
- Improved Safety: Automating dangerous or repetitive tasks reduces the risk of workplace accidents and injuries for workers.
- Higher quality: Robots, as automation tools, can perform tasks with precision and consistency that often exceeds human ability, improving the quality of products and services.
- Time release: By automating routine tasks, people can free up time and resources to focus on higher-value strategic activities.
- Competitiveness: Companies that implement automated systems can gain a competitive advantage by improving efficiency, reducing costs, and offering higher quality products and services.
DIFFERENT TYPES OF INDUSTRIAL AUTOMATION
Industrial automation has become an essential part of optimizing manufacturing and production processes in a wide range of industries. From the automotive industry to electronics or aerospace. Depending on the type of production and the activity of the industry, there are different types of industrial automation:
Fixed Automation
Fixed automation, also known as rigid automation, involves the implementation of systems designed to carry out specific tasks in a repetitive and predictable manner, in a single location. These systems are usually inflexible and designed to perform a particular task efficiently. A common example of fixed automation is an assembly line in the automotive industry, where robotic arms such as those of Kuka perform assembly tasks in sequence.
Programmable Automation
Programmable automation allows flexibility in production as systems (software) are reprogrammed or reconfigured to adapt to different products or processes. Thus, a robot can be reprogrammed to change the sequence of operations or production parameters as necessary.
Flexible Automation
Flexible automation goes a step further by enabling rapid and efficient adaptation of production systems to meet changing market demand. This is achieved by the use of modular systems and autonomous production cells that can be easily reconfigured to switch between different products or processes. An example of flexible automation is a factory that produces electronic components, where production cells adapt to changes in product design or demand.
Intelligent Automation
Intelligent automation, also known as cognitive automation or industry 4.0, relies on advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning and data analytics to optimize industrial processes. These systems are capable of making autonomous decisions and adapting in real time to changes in the production environment. An intelligent automation example is autonomous mobile robotics that uses sensors and data analysis to predict and prevent machinery failures, thereby minimizing downtime and maximizing operational efficiency.
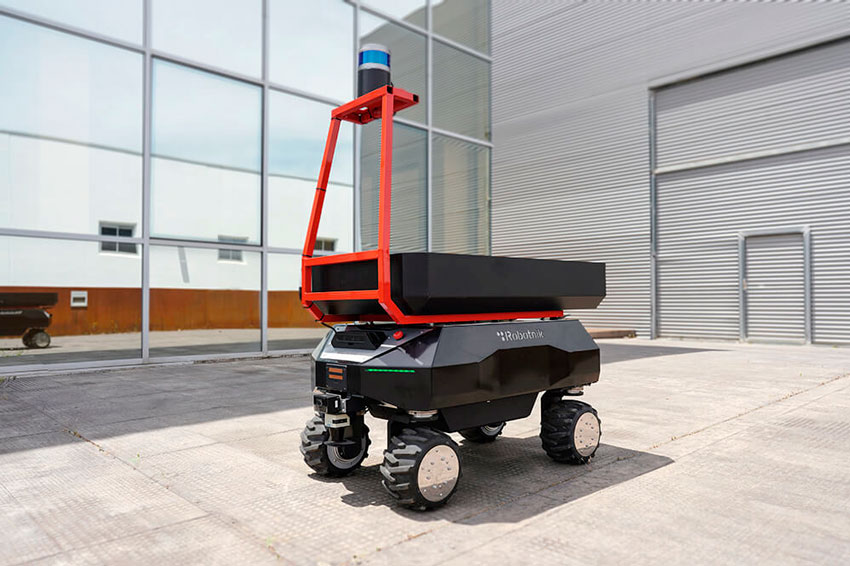

THE FUTURE OF ROBOTICS AND AUTOMATION
To conclude, Robotics and automation continue to revolutionize industries by bringing more precision, efficiency, and safety to various processes. These technologies not only transform existing industries but also pave the way for new sectors to emerge. As we look towards the future, the interplay between robotics and automation promises to further drive innovations and improvements across numerous fields.
- Integration Across Sectors: The versatility of robotics and automation allows for their application across diverse sectors, from manufacturing and healthcare to agriculture and services. This widespread adoption is crucial as it leads to uniform growth and innovation, contributing to economic stability and job creation in new areas.
- Advancements in Technology: Ongoing advancements in AI and machine learning are making automation systems more intelligent and adaptive. This evolution means that future robots will not only perform repetitive tasks but will also make complex decisions, analyze real-time data, and learn from their environments, thereby enhancing productivity and reducing human error.
- Sustainability and Efficiency: As global emphasis on sustainability intensifies, robotics and automation stand out as key enablers in making industrial processes more energy-efficient and less wasteful. Their role in smart manufacturing, for instance, can help reduce energy consumption and minimize waste production, supporting global efforts towards a more sustainable future.
- Enhancing Competitiveness: Companies that invest in automation and robotics are likely to see increased competitiveness as they can produce higher quality products at a lower cost and with greater speed. This competitive edge is essential in the global market, where efficiency and quality are paramount.
As we advance, the relationship between robotics and automation will become more integrated, influencing not just industrial settings but everyday life. The potential for these technologies to drive substantial economic and social changes makes it an exciting time for all stakeholders involved. Embracing these changes responsibly will ensure that the benefits of robotics and automation are maximized while minimizing potential downsides.
FAQs about robotics
Although the two concepts go hand in hand, they are mainly distinguished by the focus and functionality of each. Automation is a broader concept that includes robotics, but also other types of technological systems.
Industrial automation offers numerous benefits, including: increased efficiency, safety improvements, better quality of the final product or time optimization.
Many studies show the benefits of automating an industry: increased economic benefits, streamlined production processes or increased safety measures. IFR data show the evolution of the last few years.




